Latvia's Macro Profile. June 2019
Latvia's Economic Developments and Outlook
Beginning of the year saw weaker economic growth momentum
Following the cyclical upswing witnessed in the previous year, Latvia's economic growth momentum moderated at the beginning of 2019. While the Eurosystem's monetary policy stance continues to ensure very favourable financing conditions for the economy, lending is not among the key factors stimulating growth. The main sources of investment funding are corporate savings and the absorption of European Union (EU) funds. Moderation of the global demand, also reflected in a weaker demand from Latvia's trade partners, is dampening export growth in Latvia. Moreover, the prolonged uncertainty brought about by geopolitical tensions is likely to gradually manifest itself in moderating domestic investment activity and increased consumers' caution. At the same time, fiscal conditions are expected to remain supportive for the domestic economic growth.
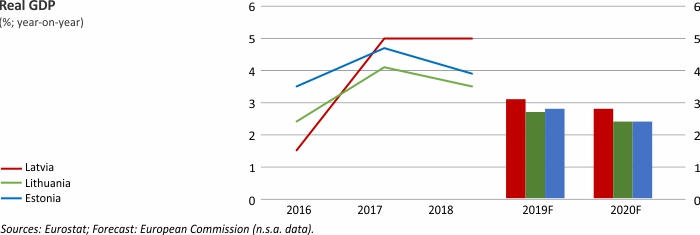
Economic growth expected to reach 2.9% this year
In its assessment of Latvia's economic outlook, Latvijas Banka took into account both weaker external demand and gradually growing caution with respect to domestic investment and consumption decisions. Moreover, one-off factors in the energy sector (related to unusual weather conditions at the beginning of this year) are also expected to have a non-negligible downward impact on economic growth in 2019. Consequently, the GDP growth forecast for 2019 has been revised downwards to 2.9%. Meanwhile, the outlook for the next years has remained broadly unchanged, with the growth rate projected to stand at around 3%.
Growth of the major economic sectors affected to a varying degree
Weakening external demand is likely to have negative implications for growth prospects in manufacturing; however, growth performance is likely to vary among its sub-sectors. High technology sectors, such as the manufacture of electronic and electrical equipment, are expected to continue to support manufacturing. Meanwhile, the rapid expansion observed so far in the wood industry is likely to moderate due to less attractive global wood prices. At the same time, significant investment in machinery and equipment is expected to alleviate supply constraints and contribute positively to the growth of manufacturing. It would also support productivity and competitiveness which is particularly important in an environment of weakening demand.
Among other sectors, transport services are expected to record only moderate growth: despite the successful development of passenger transportation by air, weaker global trade has been unfavourable for cargo transportation, also adversely affected by protectionism and Russia's decisions. Domestic demand-oriented sectors, however, are likely to be less affected in the near term, as the economic slowdown is expected to pass through to the wages dynamics with a lag. Moreover, wage growth will be supported by the public sector decisions to raise wages for certain professions. However, with consumers becoming more cautious, households are expected to further increase their savings. As a result, the growth momentum in the retail and services sectors may moderate slightly. Meanwhile, ongoing private sector investment projects as well as the availability of EU funds are likely to continue driving the activity in the construction sector in the years to come, albeit at a slower rate than before.
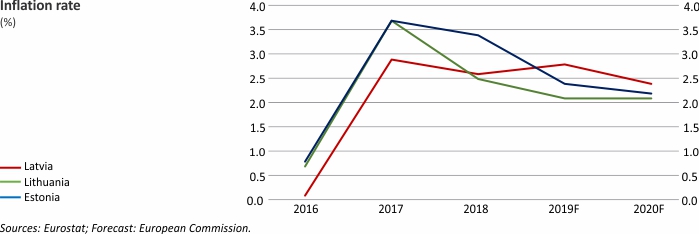
Inflation in Latvia: slightly higher than the euro area average
Latvijas Banka's inflation forecast for 2019 has remained unchanged at 2.9%. Despite a slowdown in economic growth dampening domestic pressures on consumer prices, the upturn in global food prices, mostly those of meat, has a stronger impact on inflation than previously expected. Oil price assumptions have remained broadly unchanged. However, the gradual closing of the positive output gap is likely to result in lower inflation in the coming years. Nevertheless, the ongoing income convergence is expected to retain inflation in Latvia slightly above the euro area average.
Macroeconomic indicators – actual data and forecasts
Latvijas Banka's forecasts, June 2019
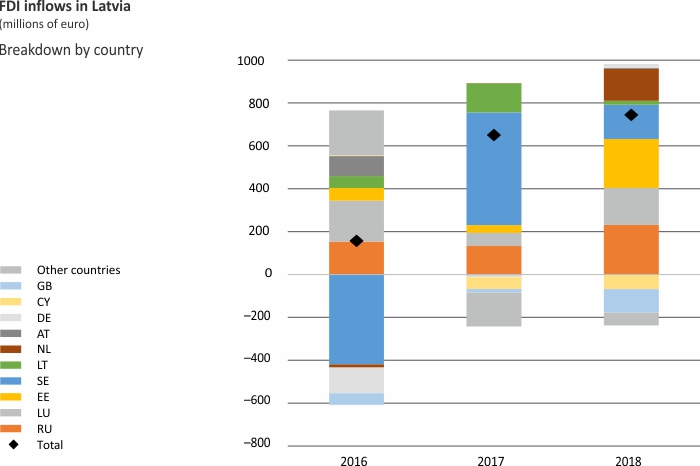
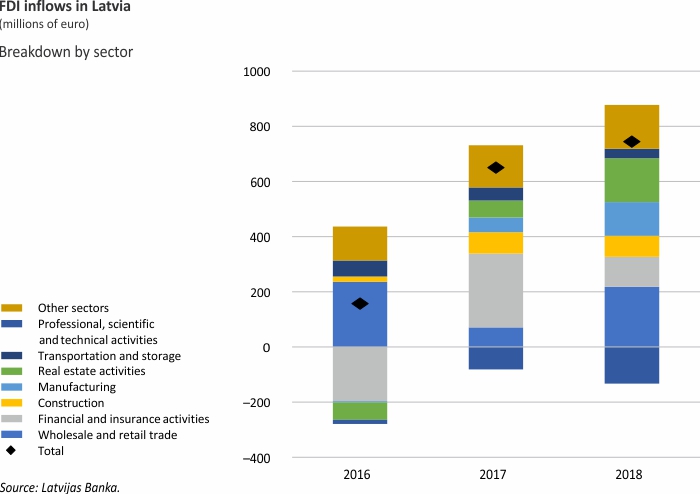
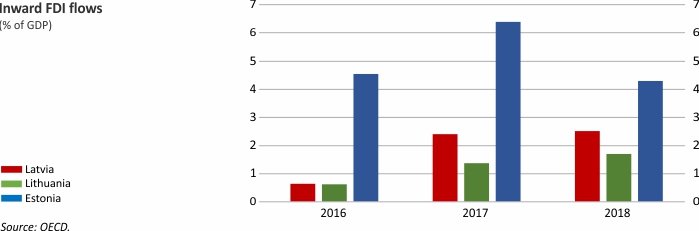
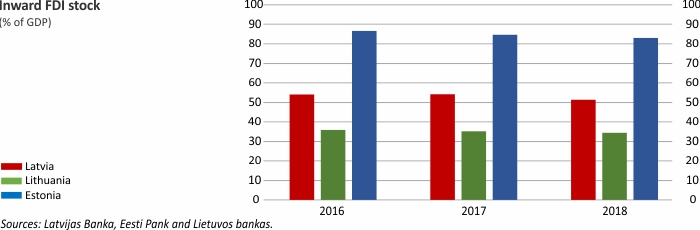
Foreign Direct Investment
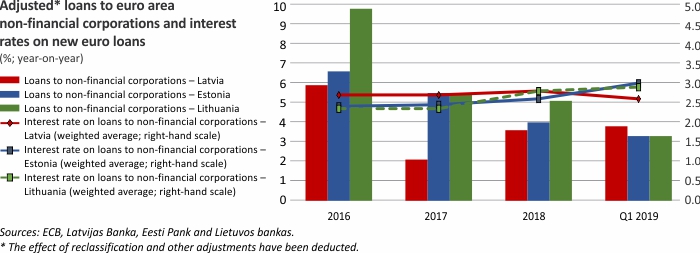
Macroeconomic Indicators: Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia
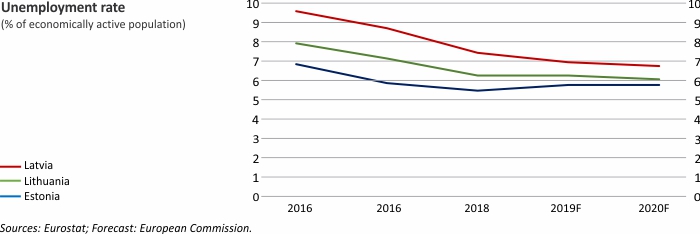
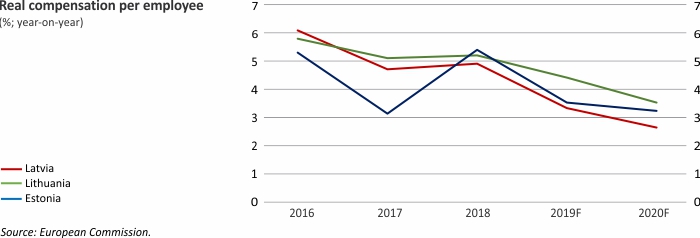
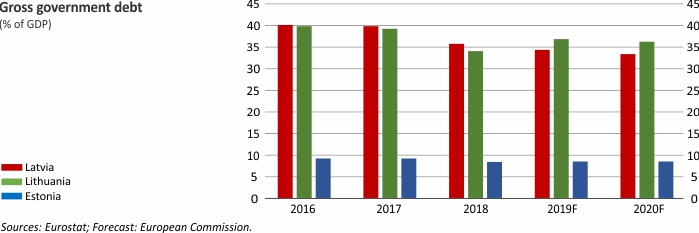
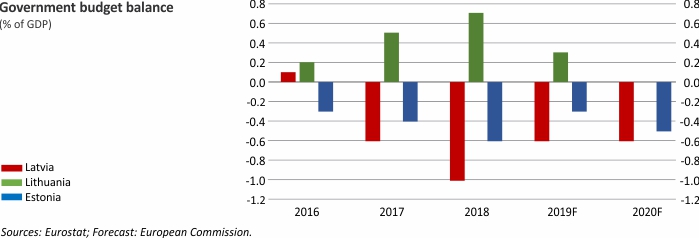
For further information on the analysis of the developments in Latvian economy, please refer to the Macroeconomic Developments Report.
Textual error
«… …»


Komentāri ( 1 )
Just brillant and easy presentation, will save a lot of time !