As Latvia moves toward participation in the euro zone, the amount of cash currency in circulation shrinks
In February, the rise in money supply was rather moderate: business deposits increased slightly whereas the rise in household deposits to a great degree corresponded to the drop in the amount of cash currency in circulation, thus having little effect on the total volume of money. There were hardly any changes in the domestic loan dynamic: the repayments of household loans were behind a slight drop in total loan portfolio whereas lending to businesses remained the same month-on-month.
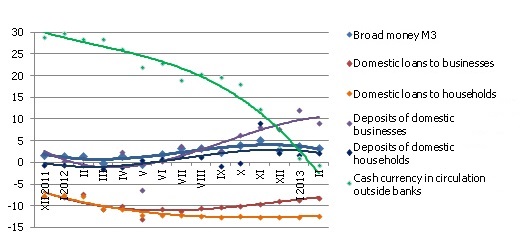
Money indicator M3, which characterizes the amount of cash and non-cash currency in the economy increased 0.6% in February, rising 3.4% year-on-year. Domestic overnight deposits, deposits redeemable at notice and – for the first time in the past nine months –deposits with a set maturity of up to 2 years grew while the amount of cash currency in circulation dropped. With the use of cash currency dropping 2.1% within a month, its annual change rate became negative for the first time in the last three years.
Illustration. Annual change in some money indicators (%)
Source: Bank of Latvia
Domestic deposits in February grew by 22.9 mil. lats in the household sector while the amount of cash currency in circulation dropped by 21.7 mil. lats, pointing to the possibility that, as the moving toward the euro zone is becoming topical, households have started reducing the role of cash currency in accruals. The clearer euro prospects along with the growing export revenue have promoted a rise in deposits in euro. If total business deposits have grown by 16.8 mil. lats total, deposits in euro have increased by 41.5 mil. lats.
The balance of loans granted to non-financial enterprises in February practically remained unchanged, whereas the loan portfolio of households shrank by 0.5%. The annual rate of change in lending to businesses was thus only minus 0.3% in February, with the indicators of banks that lost their licences in 2012 excluded from the base, whereas the total indicator for the annual drop in domestic loans improved to minus 10.1%.
Economic stability and the positive macroeconomic indicators in February promoted stability also in money supply. In the next few months substantial changes are also unlikely, yet the movement toward the euro zone will augment the role of this currency in the structure of money supply, at the same time diminishing the use of cash currency. Export revenues and the stable domestic consumption will likewise ensure a moderate rise in money supply. The stable development of the economy will counteract the sometimes excessive caution of borrowers when faced with new liabilities. It must be noted that banks have repeatedly voiced their view that such businesses have a sound basis for applying to bank loans and thus there is a potential for a rise in lending to businesses.
Textual error
«… …»






